
You can download them via:
http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?FamilyId=771AEB45-9D27-4D1F-ACD1-9B950637D64E&displaylang=en.

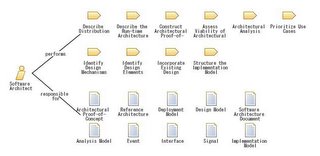

The Rational Unified Process or RUP provides a disciplined approach to software development. It is a process product, developed and maintained by Rational Software. It comes with several out-of-the-box roadmaps for different types of software projects. RUP is an iterative process that identifies four phases of any software development project. Over time, the project goes through Inception, Elaboration, Construction, and Transition phases. Each phase contains one or more iterations where you produce an executable, but perhaps incomplete system (except possibly in the Inception phase). During each iteration you perform activities from several disciplines in varying levels of detail. The above is an overview diagram of the RUP.
RUP provides guidance for all aspects of a software project. It does not require you to perform any specific activity or produce any specific artifact. It does provide information and guidelines for you to decide what is applicable to your organization. It also provides guidelines that help you tailor the process if none of the out-of-the-box roadmaps suits your project or organization.
RUP emphasizes the adoption of certain best practices of modern software development, as a way to reduce the risk inherent in developing new software. These best practices are:
1. Develop iteratively
2. Manage requirements
3. Use component-based architectures
4. Model visually
5. Continuously verify quality
6. Control change
These best practices are woven into the Rational Unified Process definitions of:
Roles – sets of activities performed and artifacts owned.
Disciplines – focus areas of software engineering effort such as Business Modeling, Requirements, Analysis & Design, Implementation, Test and Deployment.
Activities – definitions of the way artifacts are produced and evaluated.
Artifacts – the work products used, produced or modified in the performance of activities
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rational_Unified_Process